What is the digital thread and how can it help simplify the complexities in manufacturing?
Products are becoming ever more complex and great stakeholder needs and requirements. Imagine a modern jet engine or F1 car – tens of thousands of intricately connected parts working in harmony together with tight tolerances and incredible precision. The risk of failure is very high, and the effects could cascade throughout the entire system, potentially leading to unintended consequences, or even a catastrophic failure.
What are the benefits of adopting a digital thread?
Increase productivity and effectiveness
By streamlining processes and information flow across requirements capture design, engineering, and production, a digital thread can eliminate delays and rework caused by siloed data. This can lead to faster design, production cycles and improved overall effectiveness.
Improve quality assurance and reduce risk
A digital thread can allow for real-time monitoring of design or production processes and identification of potential quality issues early on. This enables proactive adjustments and reduces the likelihood of defective products reaching the customer.
Increase communication and collaboration between teams
A digital thread fosters a collaborative environment where all teams involved in the product lifecycle have access to the same information. This improves communication, reduces misunderstandings, and allows for better coordination across teams.
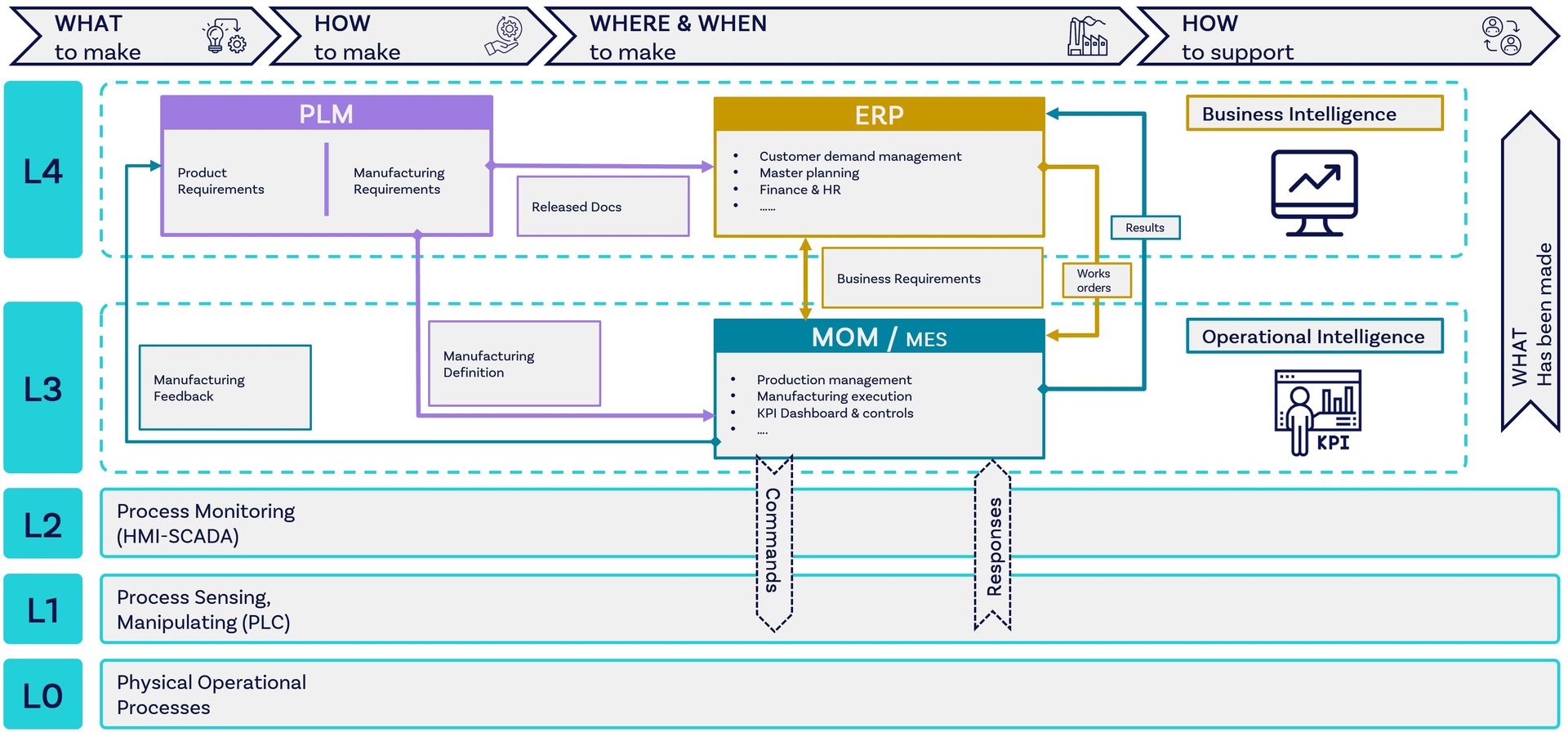
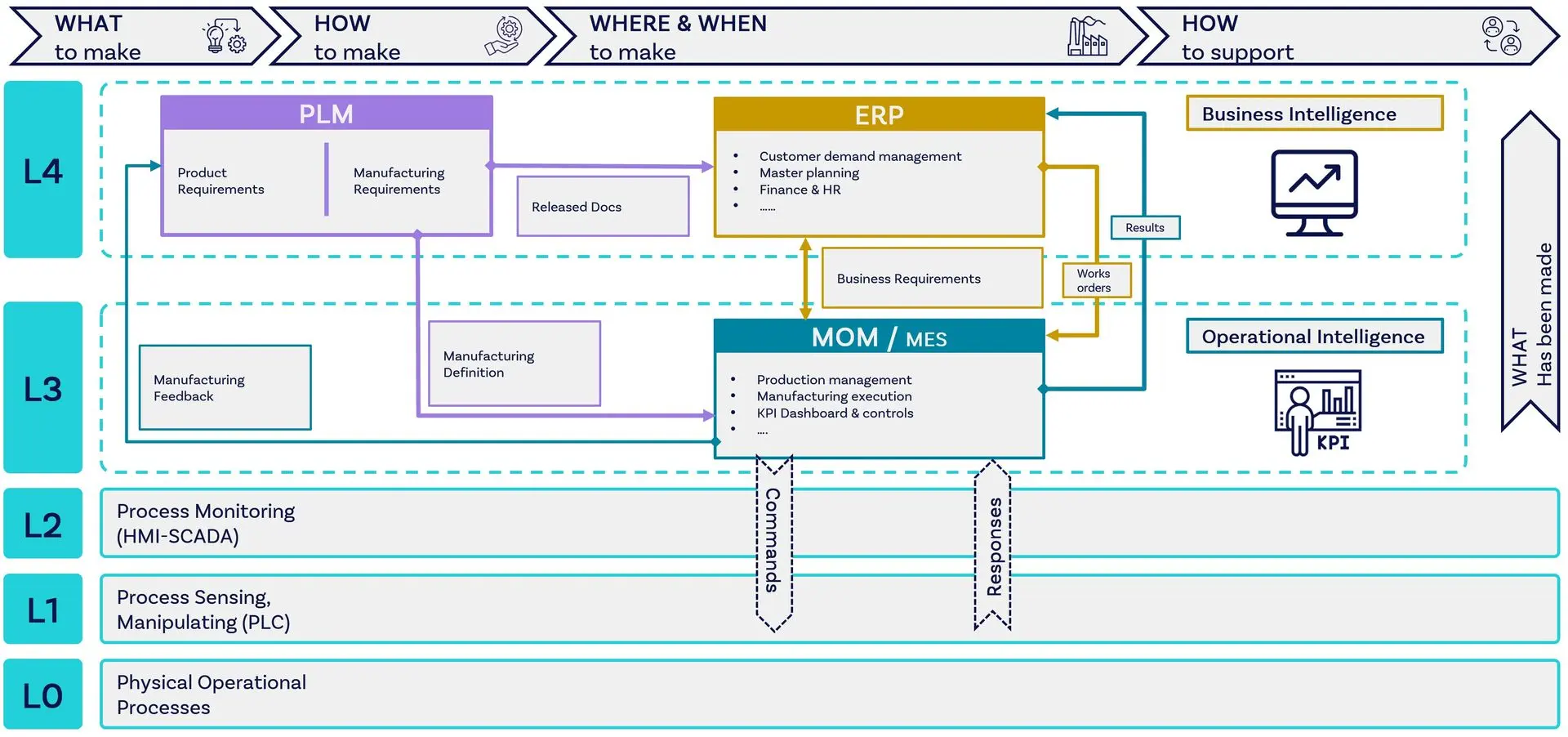
What Digital Ecosystem is needed to support a digital thread implementation?
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) System: This serves as the digital highway of the digital thread, storing and managing all product and design data throughout its lifecycle, from requirements, design inception to service and end-of-life.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System: The ERP system integrates with the PLM to provide data on supply chain, programme management, operational processes, inventory management, resources and financial aspects of production.
Manufacturing Operation Management (MoM): This system is key for managing end-to-end manufacturing processes with a view to optimising efficiency. There are many components; including for production management, performance analysis, quality and compliance, and human machine interface (HMI).
Advanced analytics tools: Extracting meaningful insights from the vast amount of data collected can require advanced analytics tools like machine learning and artificial intelligence to identify patterns, predict trends, and optimise processes.
Secure network infrastructure: A secure network infrastructure is crucial to protect sensitive data within the digital thread from cyberattacks and unauthorised access.
What are the challenges?
Cultural and adoption challenges
Implementing a digital ecosystem to enable the digital thread often requires significant changes to workflows and stakeholder mindsets, often leading to resistance to adoption. This can be combated by properly informing all employees, educating them on the importance of the digital thread.
Data issues
To realise the digital thread, there needs to be a holistic view of a product's lifecycle and ensure every stakeholder has access to the latest data. This is one of the key difficulties business face getting the right data and the right time. Much data is stored in different legacy system, excels, or no searchable formats. Often, in inconsistent data formats and a lack of standardisation, both within an organisation and across industries, which can cause confusion, poor data context and understanding.
Security concerns
An interconnected system reliant on large amounts of data are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. As with all emerging technologies, unidentified vulnerabilities will be present for malicious actors to abuse. To combat this, organisations should adopt clear data governance policies and procedures to manage access and control.